The risk of acquiring chronic illnesses like arthritis, dementia, heart disease, and diabetes increases as you age. That means that seniors need to be aware of the signs and symptoms of these common conditions. Diabetes in seniors is especially common, with one in three people aged 65+ and older developing the disease. As if that weren’t enough, many have at least one other condition at the same time.
Although you can develop diabetes at any age, it is common among older individuals. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), around 25% of Americans aged 65 and older have diabetes, with the majority of cases being type 2 diabetes. This prevalence underscores the importance of understanding and addressing the unique challenges that seniors face in managing diabetes.
The Potential Effects of Diabetes
One of the key issues for seniors with diabetes is the potential for complications. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to a range of serious health problems, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, vision impairment, and nerve damage. Type 1 and type 2 are the two most common forms of diabetes, and it’s important to understand the differences between them. Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in children and young adults and occurs when the body does not produce insulin. Individuals with type 1 diabetes require insulin therapy to manage their condition.
On the other hand, type 2 diabetes is more common in adults and is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity and physical inactivity. In type 2 diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to the insulin it produces. While both types of diabetes require careful management, understanding the distinctions between them can help seniors and their caregivers make informed decisions about treatment and self-care strategies. Complications can significantly impact a senior’s quality of life and independence. Therefore, it is crucial for seniors to actively manage their diabetes to minimize the risk of these complications.
A Multifaceted Approach to Managing Diabetes
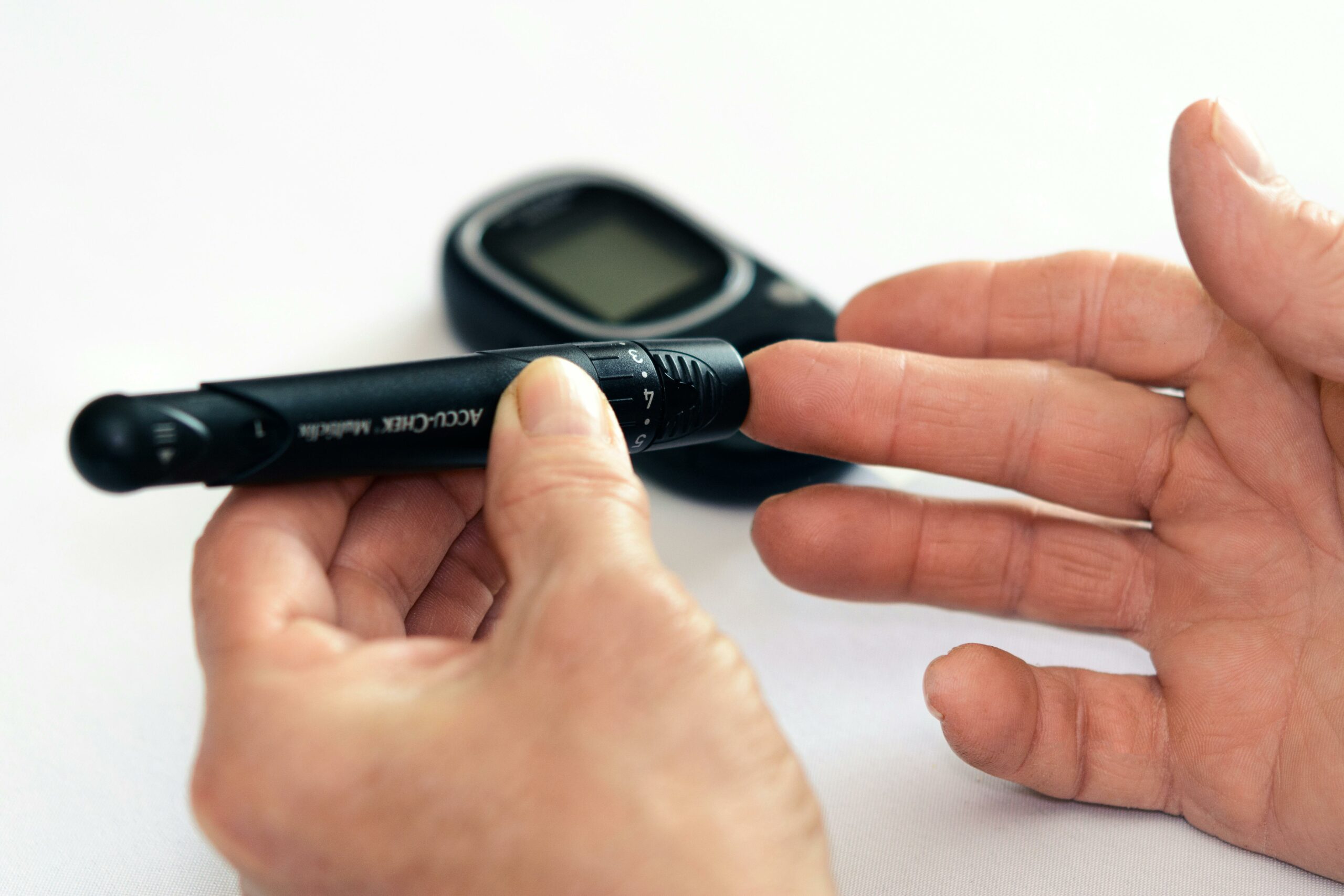
Managing diabetes in seniors often requires a multifaceted approach. This includes regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, following a well-balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and adhering to prescribed medications. Blood sugar monitoring is essential for seniors to ensure that their levels remain within a healthy range. This may involve using a blood glucose meter to check blood sugar levels at home, as well as periodic A1C testing to assess long-term blood sugar control.
Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in managing diabetes at any age, particularly for seniors. It’s important to know what and how much to eat. A cookbook designed specifically for people over the age of fifty can help prevent boredom from eating the same things day after day. At the same time, learn tips that help you manage diabetes effortlessly.
A balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help seniors control their blood sugar levels and maintain overall health. Additionally, portion control and meal timing are important considerations for seniors with diabetes. Working with a registered dietitian can help seniors develop personalized meal plans that meet their nutritional needs while managing their diabetes effectively.
Exercise
Physical activity is another important component of diabetes management for seniors. Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications. It is essential for seniors to engage in activities that are safe and appropriate for their individual fitness levels and any existing health conditions. This may include walking, swimming, tai chi, or other low-impact exercises that can be easily incorporated into a senior’s daily routine. Learn the top recommendations for senior exercise from Senior Lifestyle and get moving!
Look for age-appropriate classes in your neighborhood or opt for a DVD that you can enjoy in the privacy of your home, on your own schedule.
Medication
Medication adherence is crucial for seniors with diabetes, as prescribed medications play a key role in managing blood sugar levels and preventing complications. Seniors must understand the importance of taking their medications as directed by their healthcare providers and communicate any concerns or challenges they may have with managing their medications. In some cases, healthcare providers may need to adjust medication regimens to account for changes in a senior’s health status or lifestyle.
Having diabetes doesn’t mean you can enjoy a healthy, active lifestyle. Learn how to take your medications with you so you can enjoy more freedom.
Support & Education
In addition to these specific strategies, seniors with diabetes can benefit from ongoing education and support. Diabetes self-management programs, support groups, and educational resources can provide seniors with valuable information, practical skills, and emotional support to help them navigate the challenges of living with diabetes. Furthermore, regular communication with healthcare providers is essential for seniors to receive personalized guidance, monitor their progress, and address any concerns or complications related to their diabetes management.
Diabetes is a complex and challenging condition for seniors, but proactive management can significantly improve their health and well-being. By addressing the unique needs of seniors with diabetes through regular monitoring, a balanced diet, physical activity, medication adherence, and ongoing support, it is possible to effectively manage diabetes and reduce the risk of complications.
Ultimately, empowering seniors with the knowledge and tools to manage their diabetes can help them lead active, independent, and fulfilling lives as they age. Diabetes has become increasingly prevalent among seniors, making it crucial for this demographic to stay informed and proactive about managing their health. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in physical activity, and adhering to prescribed medications are essential for effectively managing diabetes in seniors.
